Tool policy
The activities in the test process supported by a test tool and how this will be set up depends on the tool policy pursued
in the organisation.
The tool policy is part of the test policy (see Test Policy).
The tool policy describes in a uniform manner what the purpose of the implementation of test tools must be. The use of test
tools is never an objective in and of itself. The test tool is just a means to realise a specific objective in terms of
time, money and/or quality. This is called the test tool objective. The tool policy also describes the requirements, wishes
and conditions (if any) defined for test tools. These can be based on requirements, wishes and conditions defined in the
test policy.
Furthermore, the tool policy describes the approach to be followed for the acquisition, implementation and use of tools. As
such, this part of the tool policy resembles a general plan of approach, with the difference that it represents the basis
for a long-term investment. It has been written before: the deployment of tools usually only yields a return on investment
in the long term, which is why it must be governed by a policy. A tool policy constitutes the basis on which the
organisation can base the use and implementation of tools (in the future). It is not a one-off document that is archived.
It must be updated and adapted to new developments and insights continuously.
Life cycle model for tool implementation
The implementation of test tools in a structured test process is a program with several process steps. These
process steps are incorporated in a life cycle model (see figure 1 “Life cycle model for test tool implementation”).
This defines the activities from the early start of the use of test tools through to the structural embedding in the
test process. The life cycle model distinguishes three phases: Initiation, Realisation and Operation. Each phase has
its own objectives, activities and products which are verified against the tool policy. The phases are explained in the
following sections.
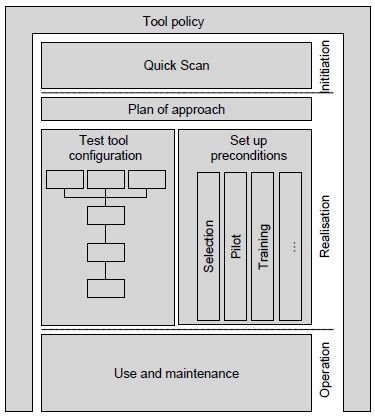
Figure 1: Life cycle model for test tool implementation
|
